The New Power Duo: Hormone Therapy + GLP-1s for Menopause Weight Gain
By: Dr. Jackie Piasta, DNP, WHNP-BC, MSCP
At Monarch Health, we know that midlife weight gain isn’t just about willpower; it's about biology. Hormones shift. Sleep changes. Stress climbs. And despite healthy habits, the belly fat seems to show up… and stay.
Let’s break down why this combination is helping so many women reclaim their health, confidence, and energy.
The Social Media Surge
GLP-1 medications like semaglutide & tirzepatide have become a popular option for weight loss, including the stubborn menopause-related weight gain.
If you’re in your 30s, 40s, or 50s and on social media, your feed is likely filled with content focusing on two hot topics: weight loss medications like semaglutide, and menopause. The algorithms are on to something real: Women gain an average of 1.5 pounds per year in midlife; a study published in the International Journal of Obesity cited an average weight gain of 12 pounds within eight years of hitting menopause. So there’s a good reason women in menopause might have weight on their minds.
It’s not just extra pounds, but also where that fat is stored, that changes in perimenopause and menopause. Women often see more accumulation around the midsection or waist as opposed to the thighs and butt. The consequences of midlife weight gain extend far beyond aesthetics, contributing to an increased risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes (T2D), and other metabolic diseases.
Combining menopause hormone therapy (MHT) with GLP-1 medications may improve weight reduction while also helping manage menopause symptoms—a win-win for many patients. However, these medications aren’t a magic bullet—and come with special considerations like potential side effects and need for long-term use.
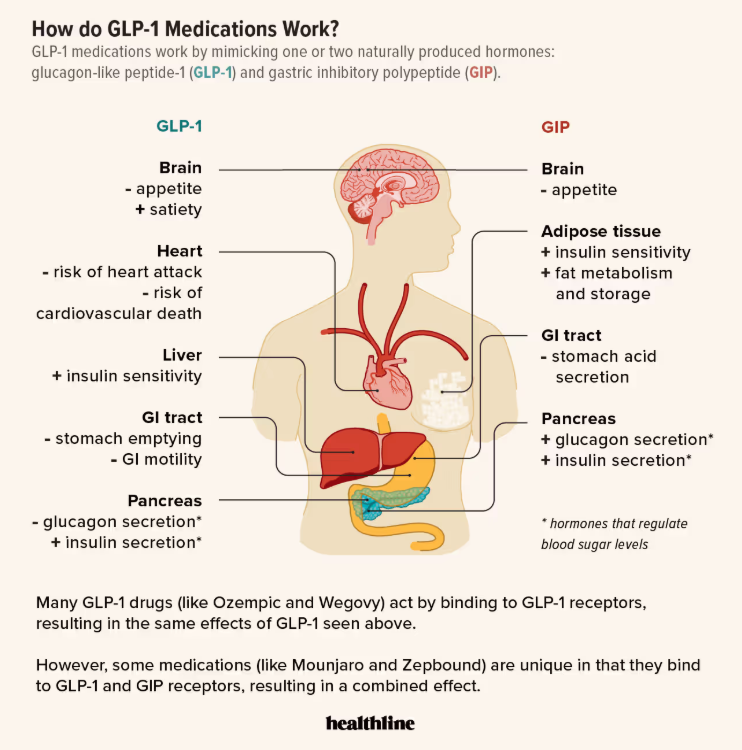
🧠 First, a Quick Refresher: What Are GLP-1s?
GLP-1s (short for glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists) are medications originally developed for diabetes in 2005, now FDA-approved for weight loss. You may recognize brand names like Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, or Zepbound.
These medications work by:
Reducing appetite and cravings (aka “food noise”)
Slowing gastric emptying, so you feel full longer
Improving insulin sensitivity and stabilizing blood sugar
⚖️ Menopause & Metabolism: Why Weight Gain Happens
You are certainly not alone!!! Up to 70% of women gain weight in perimenopause and menopause. Although there are a number of reasons for this, declining estrogen levels trigger:
Fat redistribution and more fat storage in the abdominal area (more visceral/belly fat)
Visceral fat wraps around organs and increases the risk of type 2 diabetes, fatty liver disease, and cardiovascular disease.
Increased insulin resistance
Sleep disruption, worsening appetite signals
Mood changes and less energy for movement
Even with consistent habits, women often gain 1.5–2 lb per year—often around the middle. These changes aren’t just cosmetic—they’re linked to increased risks of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and inflammation.
Reduced estrogen during menopause leads to a decrease in metabolism, causing women to burn about 250-350 fewer calories per day.
Menopause also accelerates the natural loss of muscle mass, a condition known as sarcopenia, and reduces your total daily energy expenditure, making it even harder to maintain a healthy weight or lose excess fat. The loss of muscle mass and increase in fat mass translates to more than weight gain. Because muscle is a critical player in blood sugar regulation, midlife muscle loss often goes hand-in-hand with insulin resistance, a common condition in which cells lose the ability to efficiently usher glucose out of the bloodstream to burn for energy. That inefficiency paves the way for chronic health conditions as well as further hormone disruption and weight gain.
Sleep disruption and stress are also important pieces of the puzzle that should be considered as well when determining why your body may be resistant to weight loss.
Hormone therapy (HT) can help. Studies show that estrogen therapy during menopause can attenuate visceral fat gain by as much as 60%, improve insulin sensitivity, and even help increase lean muscle mass. But true loss of the weight that has been gained already is seldom achieved with HT alone.
I like to refer to my boat analogy here. Menopause is like being in a boat with a bunch of holes. Water (weight gain) is seeping in, and hormone therapy acts like a plug for those holes. Once the holes have been plugged, well, all that water still needs bailing out. That’s where targeted lifestyle habits (ie, macro and caloric counting, resistance + cardio training) and medications approved and studied for weight loss come in.
💥 The Science Behind the Combo: GLP-1 + Hormone Therapy
A 2025 study presented at the Endocrine Society’s Annual Meeting showed that postmenopausal women who used tirzepatide (brand name Zepbound) and hormone therapy together lost significantly more weight than those on tirzepatide alone:
Average weight loss: 17% with HT, compared to 14% without
Nearly half of those on both therapies lost 20% or more of their body weight
(Source: Contemporary OB/GYN)
A 2024 study published in Menopause found similar result with semaglutide. Postmenopausal women who were on both semaglutide (the brand name for this is Ozempic) and hormone therapy (HT) lost significantly more weight than those on semaglutide alone.
At every checkpoint (which was at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months), women on HT had a higher percentage of total body weight loss. They were also more likely to achieve clinically meaningful milestones like losing 5% or 10% of their starting weight. Importantly, both groups improved their metabolic health, but the HT + GLP-1 group did better.
This suggests that HT may enhance the metabolic effects of GLP-1s, likely by improving:
Insulin sensitivity
Muscle maintenance
Sleep quality
Cortisol balance
These benefits not only support weight loss, but also help maintain it long-term.
👏 Why This Matters for You
At Monarch Health, we approach midlife care holistically. For the right patient, this combination can be transformative:
GLP-1s help reduce cravings, lower inflammation, and support meaningful weight loss.
Hormone therapy helps correct the hormonal root causes—improving sleep, mood, energy, hot flashes, and metabolism.
Used together, they can restore a sense of agency over your health and help you feel like you again.
👩⚕️ Who Might Benefit?
This combination may be a good fit if you:
✅ Are in perimenopause or menopause
✅ Are experiencing stubborn midsection weight gain
✅ Have a BMI ≥27 with other metabolic concerns or a high body fat percentage
✅ Struggle with appetite regulation or emotional eating (food noise)
✅ Have bothersome menopausal symptoms (hot flashes, poor sleep, brain fog)
✅ Are cleared for hormone therapy use
🛑 Important Considerations
Like any medication, GLP-1s come with a few side effects—most commonly nausea, constipation, or diarrhea, and reduced appetite. These are generally mild and tend to lessen over time, especially when the dose is adjusted gradually.
A few tips to support your body during treatment:
Stay well hydrated. These medications can reduce your thirst signals, so you may not feel thirsty even when your body needs fluids. Aim to drink regularly throughout the day, even if you're not craving water.
Ease into fiber. Fiber is your best ally for preventing constipation—a common side effect of GLP-1s—but it must be increased slowly. Because digestion slows on these medications, a sudden spike in fiber can lead to bloating, burping, or gas. Add fiber-rich foods or supplements gradually, and drink plenty of water to support digestion.
Skip the carbonated drinks. They can increase bloating and discomfort when digestion is already slowed.
Watch your rate of weight loss. Losing more than 1–2 pounds per week can increase the risk of gallstones, hair loss and muscle loss. This is why dosing will always be tailored to the individual.
Other important considerations:
Oral progesterone may be less effective when paired with GLP-1s due to slowed digestion. We may recommend non-oral options (like vaginal, transdermal, or IUD-based progesterone) when needed or adjust your progesterone dosing depending on your individual needs.
Not everyone is a candidate for GLP-1 therapy—especially those with a history of certain endocrine tumors or significant GI conditions.
💬 Takeaways
You deserve care that sees the whole you—not just your labs or your weight. If you're feeling frustrated, stuck, or like your body is working against you, you’re not alone. There are safe, science-backed tools that can help.
GLP-1s have become a popular weight loss medication for many people, and if you’re one of the many people coming face-to-face with menopause weight gain, you may be amongst them. They are not new. They have been around for more than 20 years and should be considered a safe, effective, and evidence-based tool, but they aren’t magic.
There’s some evidence that combining hormone replacement therapy (HRT) with GLPs can have beneficial effects on weight reduction, as well as menopause symptom management.
Not everyone is a candidate for these weight loss medications, and they can have a range of side effects.
✨ At Monarch Health, we believe menopause care is metabolic care, and we are here to help you realize your health goals with the tools seem the most congruous for you.